Horse flies, notorious for their painful bites, have long intrigued and troubled outdoor enthusiasts, particularly with their selective biting habits at night. These insects, known scientifically as members of the Tabanidae family, exhibit fascinating behaviors and preferences that make certain individuals more prone to their bites than others.
The tendency of horse flies to bite some people more than others at night is not random. It hinges on factors like body heat, carbon dioxide emission, blood type, and even the clothing color worn by individuals. These factors, combined with environmental triggers and personal attributes, play a pivotal role in determining who becomes a target for these persistent insects.
Understanding the habits and preferences of horse flies can significantly aid in mitigating their bothersome bites. Various factors, from personal to environmental, contribute to the likelihood of being bitten. This knowledge not only helps in taking preventive measures but also unravels the peculiarities of horse fly behavior, especially under the veil of night.
# Horse Flies: A Comprehensive Guide
Horse flies, a common nuisance in many parts of the world, are known for their persistent and often painful bites. These insects are more than just a simple annoyance; their unique biology and behavior reveal a complex and fascinating world. This article delves into the intricacies of horse flies, shedding light on their selective biting habits, especially at night, and the various factors that influence their behavior.
## Horse Flies: An Overview
### Biology and Behavior
Horse flies belong to the family Tabanidae, a group of insects known for their robust bodies and powerful flight. These flies are found in diverse habitats, ranging from dense forests to open grasslands. They play a significant role in the ecosystem, both as pollinators and as a food source for other animals.
#### Lifecycle and Habitats
The lifecycle of a horse fly starts as an egg, laid on vegetation near water bodies. The larvae, which are aquatic or semi-aquatic, are voracious predators, feeding on other insects and small invertebrates. After several developmental stages, they emerge as adults, ready to feed on blood. Their habitats are often dictated by the availability of suitable breeding grounds, which is why they are commonly found near water.
### Distinctive Features
#### Physical Characteristics
Horse flies are easily identifiable by their large size and distinctive eyes, which are often brightly colored and patterned. Their bodies are stout, with powerful wings that enable them to fly quickly and maneuver efficiently. The females, who are responsible for biting, possess specially adapted mouthparts that allow them to cut through skin and feed on blood.
#### Sensory Mechanisms
The sensory mechanisms of horse flies are highly developed. They have compound eyes that provide excellent vision, allowing them to spot potential hosts from a distance. Their antennae are sensitive to both chemical and physical cues in the environment, aiding them in locating prey.
## Factors Influencing Horse Fly Bites
### Body Heat and Carbon Dioxide
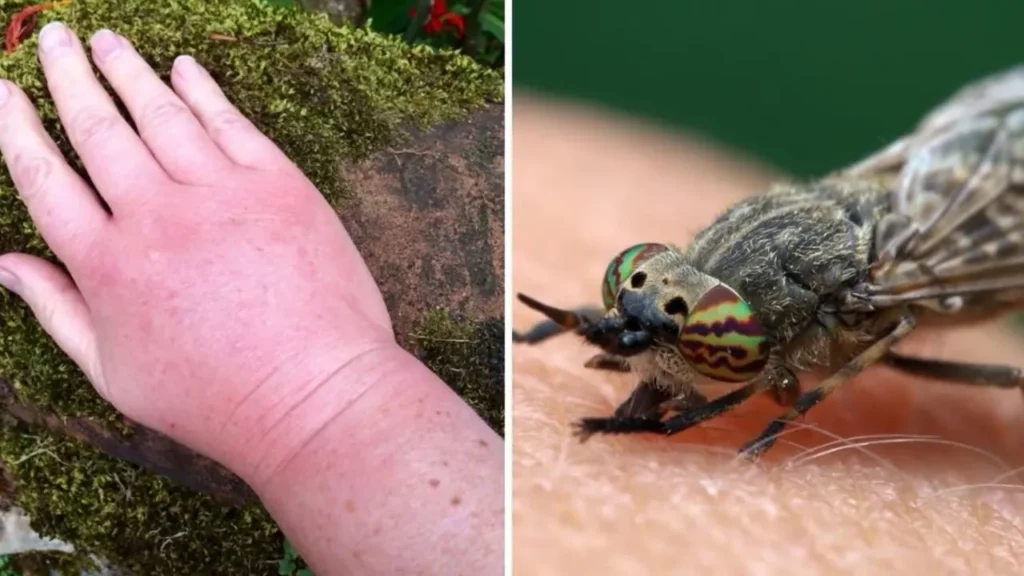

#### Role in Attraction
Horse flies are attracted to body heat and carbon dioxide, which are emitted by potential hosts. These cues help them locate animals or humans from a distance. The heat and carbon dioxide serve as signals that a blood meal is nearby, guiding the flies to their target.
### Blood Type and Skin Secretions
#### Scientific Studies and Findings
Research has shown that certain blood types and skin secretions are more attractive to horse flies. For instance, individuals with Type O blood are often more susceptible to bites than those with other blood types. Skin secretions, such as sweat and natural oils, also play a role in attracting these insects.
### Clothing and Colors
#### Impact on Visibility and Attraction
The color of clothing can significantly influence the likelihood of being bitten by horse flies. Dark colors, such as black and navy blue, are more attractive to these flies. They are drawn to contrasts and movement, which means that the type and color of clothing can either attract or deter horse flies.
The behavior of horse flies at night, and the factors that contribute to their biting habits, are complex and multifaceted. By understanding these aspects, we can better prepare and protect ourselves against these unwelcome companions. In the following sections, we will explore more about their nocturnal activities, personal factors that affect their attraction, and effective ways to prevent bites.
## Understanding Horse Fly Behavior and Attraction Factors
### Movement and Activity Levels
The frequency of horse fly bites is closely linked to the movement and activity levels of potential hosts. These flies are attracted to movement, as it indicates the presence of a living creature, which for them equates to a possible blood meal. This attraction is particularly heightened in areas where horse flies are abundant, and the movement of humans or animals can quickly draw their attention.
#### Correlation with Bite Frequency
Active individuals tend to experience more horse fly bites than those who are stationary. This is due to the flies’ ability to detect and hone in on moving targets. Consequently, people who are hiking, running, or engaging in other outdoor activities are more likely to encounter horse fly bites.
### Night-Time Behavior of Horse Flies
#### Activity Patterns at Night

While horse flies are predominantly active during the day, certain species exhibit nocturnal behaviors. This nighttime activity is influenced by various environmental factors and can vary depending on the species and habitat.
#### Differences from Daytime Behavior
The nighttime behavior of horse flies differs significantly from their daytime activities. At night, these flies rely more on sensory cues like heat and carbon dioxide, as their vision is less effective in the dark.
### Environmental Triggers
#### Temperature and Light Conditions
Temperature and light conditions are crucial environmental triggers that influence the activity patterns of horse flies. Warmer temperatures often lead to increased activity, while specific light conditions, such as moonlight, can also affect their nocturnal behaviors.
## Personal Factors Affecting Attractiveness to Horse Flies
### Genetics and Individual Chemistry
#### Research on Personal Traits
Studies have indicated that genetic factors and individual body chemistry play significant roles in attracting horse flies. Certain genetic markers and unique chemical signatures present in sweat and skin oils can make some individuals more appealing to these insects.
### Health and Diet
#### Influence on Skin Emissions
The health and diet of an individual can influence the composition of their skin emissions, such as sweat and natural oils. These changes can either increase or decrease their attractiveness to horse flies. For example, diets rich in certain fats or salts can alter body odor in a way that is more enticing to these flies.
### Personal Care Products
#### Attraction or Repellent Effects
The use of personal care products, including perfumes, lotions, and deodorants, can significantly impact the likelihood of horse fly bites. Some scents and chemicals in these products can attract horse flies, while others may repel them.
## Preventive Measures and Protection
### Clothing and Physical Barriers
#### Effective Strategies
Wearing the right clothing can be an effective strategy to prevent horse fly bites. Long sleeves, hats, and pants can provide a physical barrier against these flies. Additionally, the color and type of fabric can influence their attraction, with lighter colors generally being less appealing to horse flies.
### Repellents and Natural Solutions
#### Chemical and Organic Options
Various repellents, both chemical and natural, can offer protection against horse fly bites. Chemical repellents containing DEET are widely regarded as effective, but for those seeking more natural options, products with citronella, eucalyptus oil, or tea tree oil can also be beneficial.
In summary, understanding the factors that influence horse fly bites, such as movement, environmental triggers, personal chemistry, diet, and the use of specific products, is crucial in minimizing the risk of these unpleasant encounters. By implementing appropriate preventive measures and being mindful of personal and environmental factors, one can significantly reduce the likelihood of being bitten by horse flies, especially during their more active periods at night.
## Advanced Strategies to Deter Horse Flies

### Behavior Modifications
Modifying one’s behavior can be a crucial step in reducing horse fly bites. By understanding the factors that attract these pests, individuals can take proactive measures to make themselves less appealing targets. Simple changes in daily routines and outdoor activities can have a significant impact.
#### Reducing Attraction Factors
– Limit outdoor activities during peak horse fly hours, typically the warmest and brightest parts of the day.
– Avoid areas known for high horse fly populations, such as near water bodies or in dense forests.
– Reduce excessive movement and rapid activities in areas where horse flies are common, as these insects are attracted to movement.
### Case Studies and Anecdotes
#### Personal Experiences
The experience of horse fly bites varies widely among individuals. For some, these encounters are a rare nuisance, while others find themselves frequently targeted. Personal anecdotes often highlight the role of individual factors, such as body chemistry and activity levels, in these varied experiences.
#### Varied Reactions and Situations
Reactions to horse fly bites also differ. While some individuals experience minimal discomfort, others may have more severe reactions, including swelling and intense itching. This variation can be attributed to individual sensitivities and immune responses.
### Scientific Observations
#### Insights from Research
Scientific research provides valuable insights into the behavior and preferences of horse flies. Studies have focused on aspects like sensory mechanisms, environmental triggers, and the impact of human factors on these insects’ behavior. This research not only enhances our understanding of horse flies but also informs the development of more effective prevention and control strategies.
### Emphasis on Understanding and Prevention
The key to reducing horse fly bites lies in understanding their behavior and the factors that attract them. By being aware of these elements, individuals can adopt preventive measures that effectively reduce the risk of bites. This includes choosing the right clothing, using repellents, and modifying behavior and activities to make oneself less attractive to these pests.
### Encouraging Further Awareness and Personal Care
It’s essential to encourage ongoing awareness about horse flies and their behavior, especially for those who spend a significant amount of time outdoors. Personal care and vigilance can go a long way in preventing uncomfortable and potentially harmful encounters with these insects. Staying informed about the latest research and recommendations can help individuals protect themselves more effectively.
In summary, the challenge posed by horse flies requires a multifaceted approach. By combining behavior modifications, an understanding of personal and environmental factors, and the use of protective measures, one can significantly reduce the likelihood of horse fly bites. As research continues to unveil new insights into these insects’ behavior, adapting our strategies and maintaining awareness will remain crucial in managing our interactions with them.
How do I stop horse flies from attacking me?

To reduce the likelihood of horse fly attacks, you can implement a combination of strategies focused on making yourself less attractive to these insects and physically preventing them from biting. Here are some effective measures:
1. **Wear Appropriate Clothing**: Horse flies are attracted to dark colors, so wearing light-colored clothing can make you less appealing to them. Cover as much skin as possible with long-sleeved shirts and long pants. Tightly woven fabrics are better at preventing bites.
2. **Use Repellents**: Apply insect repellents that contain DEET, picaridin, or IR3535. These are effective against a wide range of biting insects, including horse flies. Natural alternatives like citronella or eucalyptus oil can also be used, but they may be less effective and require more frequent application.
3. **Avoid Peak Hours and Locations**: Horse flies are most active during the warmest and brightest parts of the day. If possible, avoid outdoor activities during these times. Also, stay away from areas known to have high horse fly populations, such as near water bodies or in dense vegetation.
4. **Physical Barriers**: Use physical barriers such as head nets or hats with nets when in areas with high horse fly activity. These barriers can be especially useful for protecting the face and neck, areas commonly targeted by horse flies.
5. **Minimize Scent and Sweat**: Horse flies are attracted to the carbon dioxide and lactic acid in sweat, as well as certain scents. Avoid heavy exertion when in horse fly-prone areas and consider using unscented personal care products.
6. **Stay Calm and Move Slowly**: Quick movements can attract horse flies. If you notice horse flies in the area, try to move calmly and slowly to make yourself less noticeable.
7. **Keep the Area Clean**: In your immediate environment, reduce factors that may attract horse flies, like open garbage or food residues.
Remember, while these measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of horse fly bites, it might not be possible to completely eliminate the risk, especially in areas where these insects are prevalent.
## Frequently Asked Questions
### Why Are Horse Flies Attracted to Some People More Than Others?
Horse flies are attracted to certain individuals more due to differences in body heat, carbon dioxide emission, and other personal factors like blood type and skin secretions. These elements make some people more appealing to horse flies, explaining the variation in bite frequency among different individuals.
### Do Horse Flies Bite More During Night Time?
Horse flies are typically more active during the day, but some species exhibit increased biting behavior at night, especially in warmer climates or during full moon phases. Environmental conditions like temperature and light can influence their nocturnal activity.
### Can Clothing Color Affect Horse Fly Bites?
Yes, clothing color can affect horse fly bites. Darker colors tend to attract horse flies more than lighter shades. They are visually attracted to contrasts and movements, so the color and type of clothing can influence their biting behavior.
### Are There Effective Natural Repellents Against Horse Flies?
There are natural repellents that can be effective against horse flies. Ingredients like citronella, eucalyptus oil, and tea tree oil are known to repel these insects. However, their effectiveness can vary, and it’s often recommended to use them in conjunction with other preventive measures.
### How Can One Reduce the Risk of Horse Fly Bites?
Reducing the risk of horse fly bites involves a combination of measures like wearing appropriate clothing, using chemical or natural repellents, avoiding areas with high horse fly activity, and understanding personal factors that might increase attractiveness to these insects.
## Conclusion
Horse flies, with their selective biting habits, pose a unique challenge, especially at night. Recognizing the factors that contribute to their biting preferences is the first step towards effective prevention. From body heat to clothing color, various elements play a role in making certain individuals more susceptible to bites.
Implementing preventive strategies, such as appropriate clothing, repellents, and behavioral modifications, can significantly reduce the likelihood of being bitten. These measures, coupled with an understanding of personal and environmental factors, are key in managing encounters with these persistent insects.
In conclusion, the interaction between horse flies and humans is complex and influenced by a myriad of factors. By understanding these intricacies, one can better prepare for and protect against these unwelcome nighttime intruders, ensuring a more comfortable and enjoyable outdoor experience.