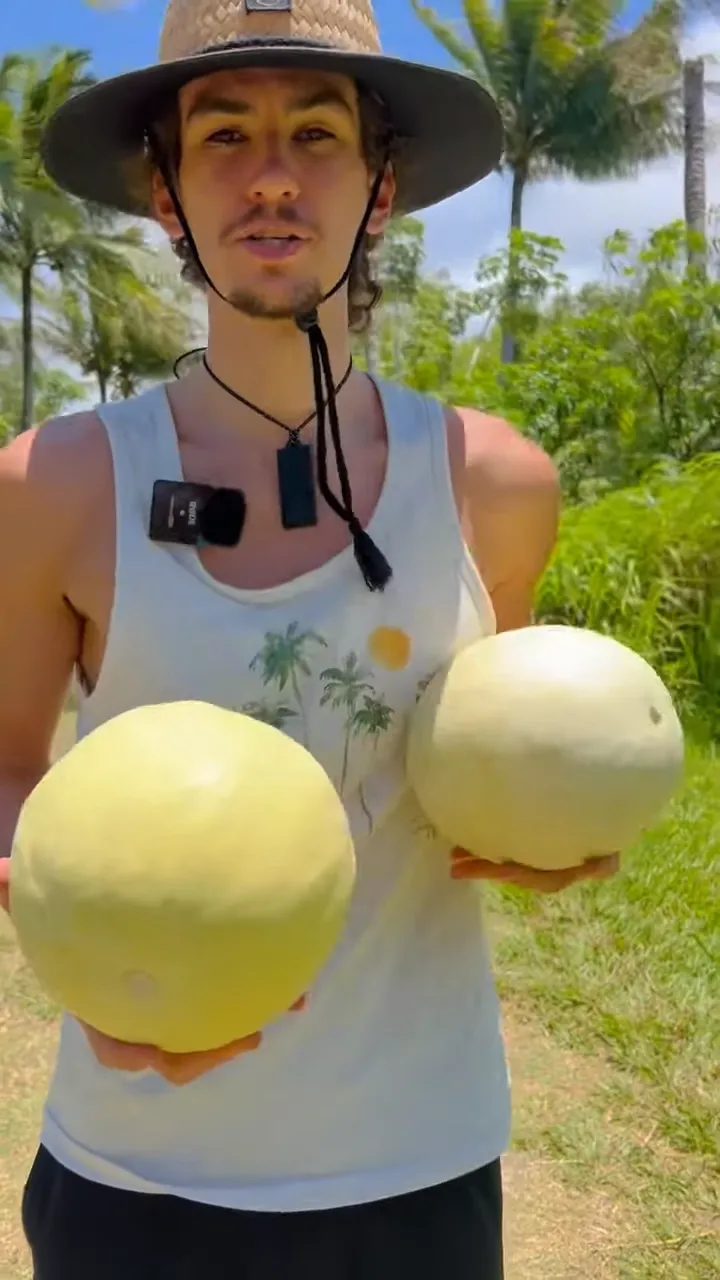
Honeydew melons, with their pale green flesh and smooth, creamy texture, have long captivated the taste buds of fruit lovers around the world. These melons are not only a staple in summer salads and fruit bowls but also hold a place of intrigue in the botanical world. The curiosity about their growth, particularly whether they grow on trees, is a topic of frequent discussion among enthusiasts and casual consumers alike.
Contrary to some popular beliefs, honeydew melons do not grow on trees. They are, in fact, grown on the ground, as a part of sprawling vines. These vines, belonging to the Cucurbitaceae family, are akin to those of cucumbers and squashes. Honeydews develop from flowers and mature on these vines, benefiting from the nutrients and support the vine system provides.
The growth of honeydew melons on vines, rather than trees, plays a crucial role in their development and the characteristics they are known for. These melons require specific conditions to thrive, including ample sunlight, well-drained soil, and careful tending. The vine-grown nature of honeydews contributes significantly to their size, taste, and texture, making them a unique and cherished addition to the world of fruits.
Common Misconceptions About Honeydew Melon Growth
One prevalent myth surrounding honeydew melons is that they grow on trees, akin to fruits like apples or pears. This misconception likely arises from a lack of familiarity with the growth patterns of various fruits. In reality, honeydews develop on the ground, supported by sprawling vines. This ground-based growth affects various aspects of the fruit’s development, from its size and shape to the texture of its flesh.
Honeydew Melon Basics
Description and Characteristics of Honeydew Melons
Honeydew melons are distinguished by their smooth, firm outer rind and their lush, pale green flesh. They typically have a spherical or slightly oval shape and can vary in size. The skin, transitioning from green to a more yellowish tone as the fruit ripens, is noticeably smooth without the netting found on cantaloupes. Inside, the flesh is juicy, subtly sweet, and devoid of fibers, offering a refreshing taste that is less sugary than that of many other melon varieties.
Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits
Nutritionally, honeydew melons are a powerhouse of hydration and essential nutrients. They are rich in:
- Vitamin C: Essential for immune system support and skin health.
- Potassium: Crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health and proper muscle functions.
- Dietary fiber: Aids in digestion and promotes a feeling of fullness, contributing to weight management.
- Low in calories: Makes them an excellent choice for a healthy diet plan.
The high water content in honeydews also makes them perfect for hydration during hot weather or after exercise. Additionally, the presence of antioxidants in honeydew melon helps combat oxidative stress, potentially lowering the risk of certain chronic diseases.
Honeydew Growth Habitat
Natural Habitat and Growing Conditions

Honeydew melons thrive in warm, temperate climates with ample sunlight. They require well-drained, fertile soil with a neutral to slightly acidic pH. Regular watering is crucial, especially during the initial growth stages and fruit development. However, overwatering or poor drainage can lead to root rot or other diseases.
Comparison with Other Melon Varieties
When compared to other popular melons like cantaloupe or watermelon, honeydews have certain distinct growing requirements. While all these varieties prefer similar climates, honeydews often need a longer maturation period. They are more sensitive to cold temperatures, and their smooth skin makes them somewhat more susceptible to pests and diseases than the netted varieties like cantaloupes.
Understanding the Plant
Botanical Classification of Honeydew Melons
Honeydew melons, scientifically known as Cucumis melo var. inodorus, belong to the Cucurbitaceae family, which includes squashes, cucumbers, and other gourds. They are categorized separately from the muskmelons due to the lack of musky aroma and the smoothness of their rind.
Structure and Growth Pattern of the Plant
The honeydew melon plant features sprawling vines that can extend several feet across the ground. The leaves are large, lobed, and provide necessary shade and protection for the developing fruits. The vines possess tendrils that help them grip onto nearby structures for support, although they do not climb like some other vine plants.
Growth Cycle of Honeydew
Seed Germination and Early Growth Stages
The journey of a honeydew melon begins with the germination of seeds, typically in warm, moist soil. Germination can take anywhere from 3 to 10 days, depending on the conditions. Once sprouted, the seedlings require adequate sunlight and water to grow. The first true leaves emerge shortly after, marking the start of significant growth.
### Flowering and Fruit Development Process
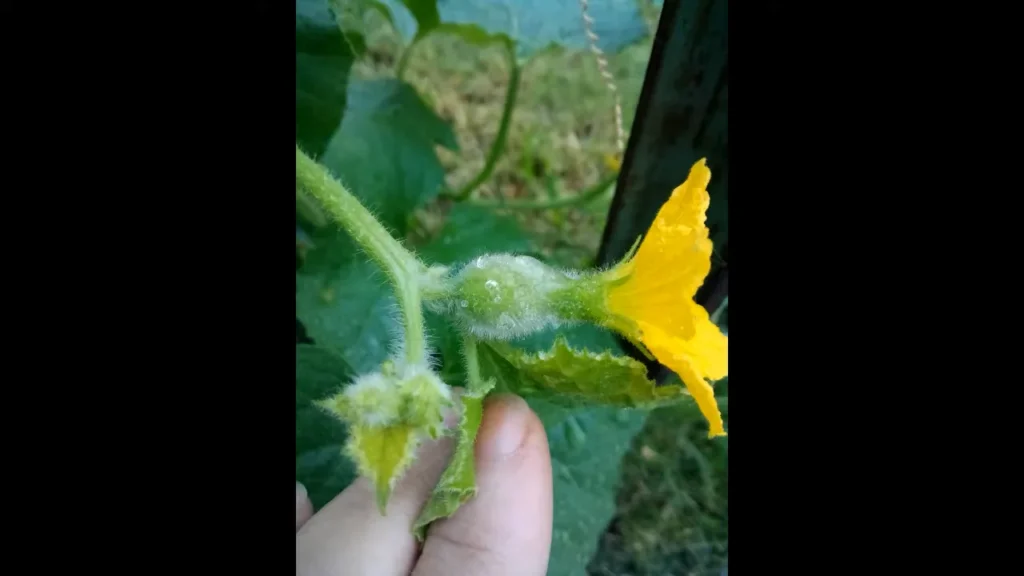

Honeydew melons, known for their sweet and refreshing taste, undergo a fascinating flowering and fruit development process. The journey begins with the plant producing yellow, bell-shaped flowers. These blossoms are typically monoecious, meaning the same plant bears both male and female flowers. The male flowers appear first, followed by the female ones, which can be identified by a small bulge at their base, the ovary, which eventually develops into the fruit.
Pollination is a critical step in this process. Bees and other pollinating insects play a vital role in transferring pollen from male to female flowers. Once pollination occurs, the female flower starts the transformation into a honeydew melon. The initial growth is rapid, as the fruit swells and begins to take shape.
Throughout this phase, the fruit requires ample water and nutrients to develop properly. The melons grow larger and gradually change in color as they mature. The exterior, initially a vibrant green, becomes paler and adopts the characteristic smoothness of a mature honeydew.
### Cultivation Practices
#### Farming Methods for Honeydew Melons
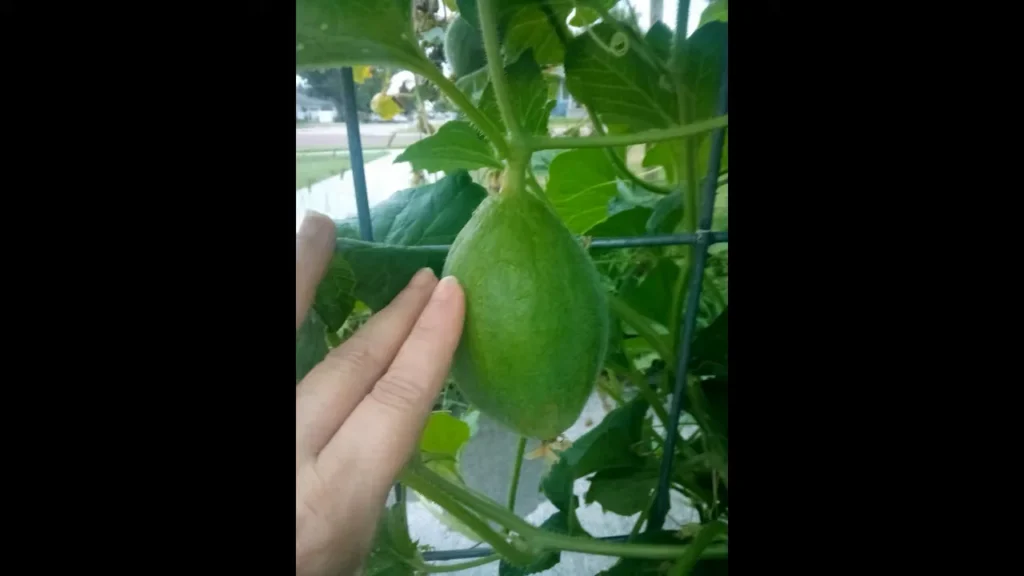

Honeydew melons are typically grown in fields and require specific conditions to flourish. The most common method involves planting seeds directly into the soil or starting them in nurseries and transplanting the seedlings to open fields. Crop rotation is a key practice among farmers to maintain soil health and prevent disease.
#### Ideal Climate and Soil Conditions
For optimal growth, honeydew melons prefer warm, temperate climates with plenty of sunlight. They thrive in temperatures between 65°F and 75°F. The soil should be fertile, well-drained, and rich in organic matter. A pH level ranging from 6.0 to 6.8 is ideal for honeydew cultivation.
### Harvesting Honeydew Melons
#### Signs of Maturity and Readiness for Harvest
Determining the right time to harvest honeydew melons is crucial for ensuring their best taste and texture. Signs of maturity include a change in color from green to creamy yellow and the development of a smooth, waxy surface. Another indicator is the ease with which the stem can be separated from the fruit.
#### Harvesting Techniques and Post-Harvest Handling
Harvesting is typically done by hand, with careful attention to avoid damaging the fruit. Once harvested, honeydews should be cooled as quickly as possible to maintain freshness. They are then stored and transported under controlled temperatures to prevent over-ripening and maintain their quality.
### Common Myths Debunked
#### Misconceptions About Honeydew Growth
A prevalent myth is that honeydews are difficult to grow. In reality, with the right conditions, they can be quite resilient. Another misconception is regarding their water needs; while they do require regular watering, over-watering can be detrimental.
#### Clarifying Facts Versus Fiction
Honeydews do not grow on trees, as some might believe. They grow on ground vines and require specific growing conditions, including ample space, to develop properly.
### Environmental Impact
#### Sustainability in Honeydew Melon Farming
Sustainable farming practices are vital in honeydew cultivation. This includes responsible water management, using organic fertilizers, and employing integrated pest management strategies to reduce the environmental impact.
#### Ecological Considerations and Impact
The cultivation of honeydew melons can contribute to soil health if managed responsibly. Crop rotation and organic farming practices help maintain the ecological balance and promote biodiversity.
### Honeydew in Cuisine
#### Popular Uses in Cooking and Recipes
Honeydew melons are versatile in culinary uses. They can be eaten fresh, added to fruit salads, blended into smoothies, or used in desserts. Their sweet flavor complements both sweet and savory dishes.
#### Pairing with Other Foods and Flavors
Honeydews pair well with other fruits like berries, citrus, and grapes. They also complement cheeses, especially feta and mozzarella, and can be used in salads with greens and vinaigrette. The melon’s sweetness balances well with the tanginess of dressings and the saltiness of cheese, making it a delightful addition to various recipes.
### FAQs on Honeydew Melons
#### What is the Best Season to Grow Honeydew Melons?
The ideal season for growing honeydew melons is late spring to early summer. This period provides the warm temperatures and long daylight hours necessary for optimal growth and fruit development.
#### How Can You Tell When a Honeydew Melon is Ripe?
A ripe honeydew melon emits a subtle, sweet aroma and has a slightly soft end opposite the stem. The rind color also shifts from green to a creamy yellow as it ripens.
#### Do Honeydew Melons Continue to Ripen After Being Picked?
Yes, honeydew melons can continue to ripen after being harvested. However, their sugar content does not increase post-harvest, so it’s essential to pick them when they are near maturity for the best taste.
#### How Should Honeydew Melons be Stored?
Unripe honeydew melons can be stored at room temperature. Once ripe, they should be refrigerated and consumed within a few days for optimal freshness and flavor.
#### Are Honeydew Melons High in Sugar?
Honeydew melons have a natural sweetness but are not excessively high in sugar. They provide a healthy balance of natural sugars and essential nutrients.
#### Can Honeydew Melons be Grown in Containers?
Growing honeydew melons in containers is possible but challenging due to their sprawling vine nature and need for ample space. It requires large containers and careful management of water and nutrients.
#### Expert Answers and Tips
Growing honeydew melons can be a rewarding experience for both novice and experienced gardeners. Key tips include choosing a sunny location, ensuring well-drained soil, and regular watering while avoiding over-saturation. Monitoring for pests and diseases is crucial for healthy growth. Training the vines on trellises can help manage space and improve air circulation around the plants.
### Recap of Key Points
Honeydew melons are a delightful and nutritious fruit, grown on ground vines rather than trees. They thrive in warm climates with well-drained soil and require careful attention to watering and pest control. The fruit matures on the vine and can be identified as ripe by its color change, softness, and aroma. Sustainable cultivation practices not only yield delicious honeydews but also contribute positively to the environment.
Honeydew melons offer versatility in culinary uses, from fresh consumption to incorporation in various dishes. They pair wonderfully with other fruits, cheeses, and even in savory salads, providing a burst of sweetness that enhances the overall flavor profile of a dish.
### Encouragement to Explore and Enjoy Honeydew Melons
Honeydew melons are not just a tasty addition to your diet but also a fascinating fruit to grow and learn about. Their unique growth process, nutritional benefits, and culinary versatility make them a fruit worth exploring. Whether you’re a gardener interested in growing your own honeydews or a culinary enthusiast looking to incorporate more fruits into your meals, honeydew melons offer a world of possibilities.
Engaging with the process of growing, harvesting, and preparing honeydew melons can deepen your appreciation for this remarkable fruit. It’s an opportunity to connect with nature, understand the intricacies of plant growth, and enjoy the fruits of your labor in the most literal sense.
In the kitchen, experiment with honeydew melons in various recipes. Their sweet, refreshing flavor can elevate a simple fruit salad, add a surprising twist to a savory dish, or be the star ingredient in a summer beverage. The possibilities are endless, and each experiment can lead to new, delightful discoveries.
Ultimately, honeydew melons are more than just a seasonal treat. They represent a journey from seed to plate, encompassing the wonders of nature, the satisfaction of cultivation, and the joy of culinary creativity. So, embrace the journey and enjoy every slice of this delicious, nourishing fruit.
Where does honeydew come from?

Honeydew melons, known for their sweet and refreshing taste, have a long and interesting history. They are believed to have originated in West Africa or in the Middle East, specifically in Iran (formerly Persia). Historical evidence suggests that they have been cultivated for thousands of years, and their popularity spread along trade routes into Egypt and the Mediterranean region.
The ancient Egyptians are known to have cultivated honeydew melons, and they were valued in these early cultures not only for their flavor but also for their hydrating properties, especially important in arid regions. Over time, the cultivation of honeydew melons spread to other parts of Europe and eventually to the New World with the help of explorers and traders.
In the United States, honeydew melons were relatively unknown until the early 20th century. Their introduction and rise in popularity in the U.S. are often credited to agricultural explorers who brought back varieties of these melons from international expeditions. Today, honeydew melons are grown in many parts of the world, with China, Turkey, and the United States being some of the leading producers.
The honeydew melon is a part of the Cucurbitaceae family, which also includes cucumbers, pumpkins, and other types of melons like cantaloupe. This family of fruits is characterized by their vine-growing habit and their need for warm growing conditions, which is why they are found in abundance in regions with warm to temperate climates.
### FAQs on Honeydew Melons2
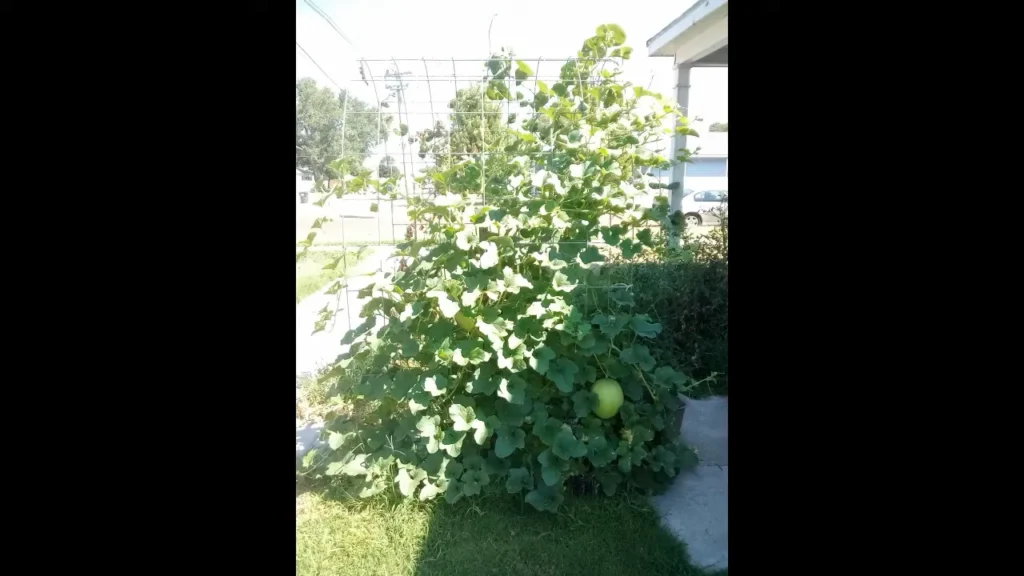

#### How Long Does It Take for a Honeydew Melon to Mature?
It typically takes about 80 to 100 days for a honeydew melon to reach full maturity after planting. The exact time can vary based on climate, soil conditions, and the specific variety of honeydew.
#### Can Honeydew Melons Grow in Any Climate?
Honeydew melons thrive best in warm, temperate climates. They need a long growing season with plenty of sunshine and moderate temperatures. While they can be grown in various regions, extreme cold or heat can hinder their growth.
#### What Is the Best Way to Store Honeydew Melons?
After harvesting, honeydew melons can be stored at room temperature until they ripen. Once ripe, they should be refrigerated and consumed within a week for the best flavor and texture.
#### Are Honeydew Melons Related to Watermelons?
Yes, honeydew melons are related to watermelons. Both are members of the Cucurbitaceae family, which also includes cucumbers, squashes, and pumpkins.
### Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey of honeydew melons from vine to table is a fascinating one, marked by specific growth requirements and careful cultivation. These melons, treasured for their sweet flavor and hydrating properties, are a testament to the wonders of plant growth and agricultural practices. As we savor each bite of this delightful fruit, we are reminded of the intricate processes and dedicated efforts that bring such natural delights to our tables.
Furthermore, understanding the growth and cultivation of honeydew melons not only enriches our appreciation for this fruit but also highlights the importance of sustainable farming practices. It encourages us to explore and support agricultural methods that are in harmony with nature, ensuring the availability of fresh, nutritious produce for generations to come.
Finally, the world of honeydew melons, with its blend of botanical science and culinary delight, invites us to explore beyond the surface. It’s a world where every vine tells a story, every melon holds a history, and every slice is a celebration of nature’s bounty.


